MPLS BGP-LU (Label Unicast) is used to extend label-switched paths (LSPs) beyond the boundaries of a single IGP or LDP domain. In traditional MPLS networks, label distribution depends on protocols such as LDP or RSVP, which operate only within the same routing domain. However, in large-scale or multi-domain networks, these protocols cannot directly exchange labels across different areas or autonomous systems. BGP-LU solves this limitation by using BGP itself to carry both routing and label information, enabling seamless end-to-end MPLS connectivity between separate domains.
Key Benefits of BGP-LU
BGP Label Unicast (BGP-LU), defined under AFI/SAFI 1/4 for IPv4 and AFI/SAFI 2/4 for IPv6, extends MPLS label distribution beyond a single IGP or LDP domain.
- Facilitates label-switched path (LSP) continuity across separate IGP or AS boundaries.
- Eliminates the need for LDP adjacency between different routing domains.
- Simplifies the control plane by using BGP as both the routing and label distribution protocol.
- Scales efficiently in large service provider backbones with complex domain structures.
- Supports advanced use cases such as Inter-AS MPLS VPN (Option C) and Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) models.
- Provides IPv4 and IPv6 interoperability through AFI/SAFI 1/4 and 2/4 address families.
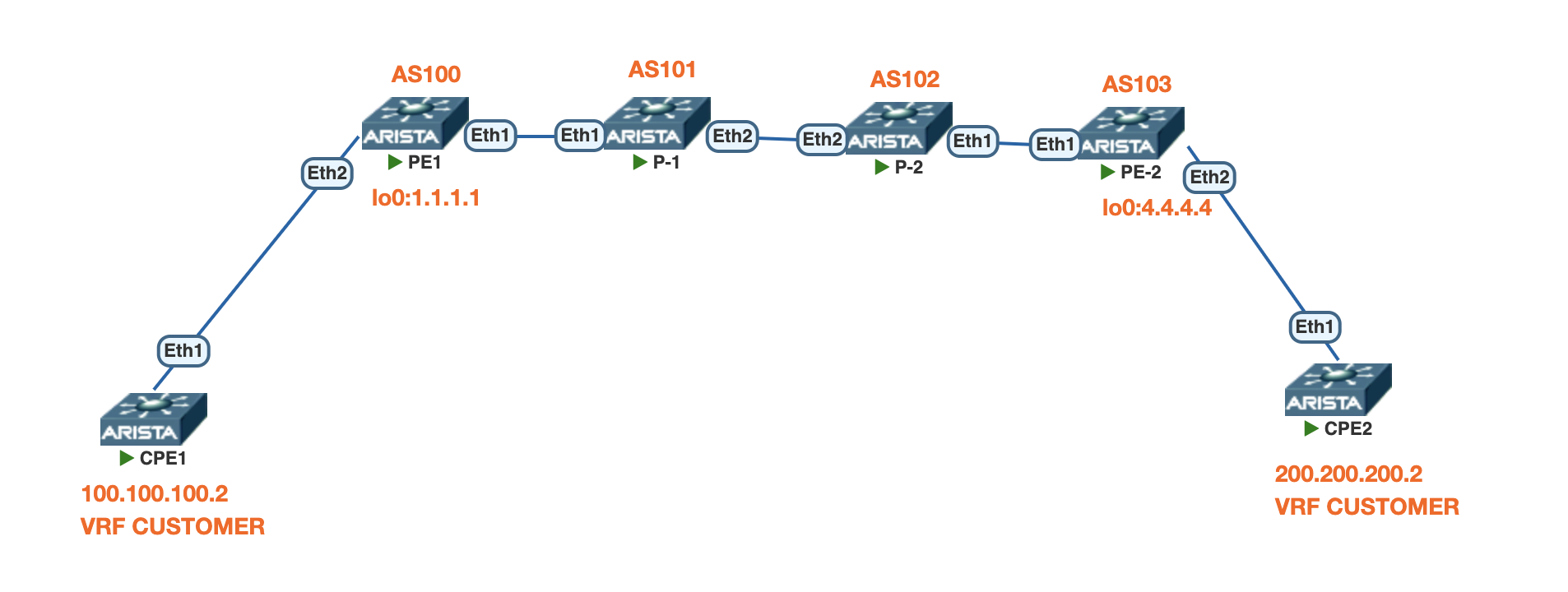
Topology
Design Details
As shown in the topology, there are four MPLS-enabled Arista routers: PE1, P1, P2, and PE2, with AS numbers 100, 101, 102, and 103, respectively. For simplicity, we used eBGP between all adjacent routers.
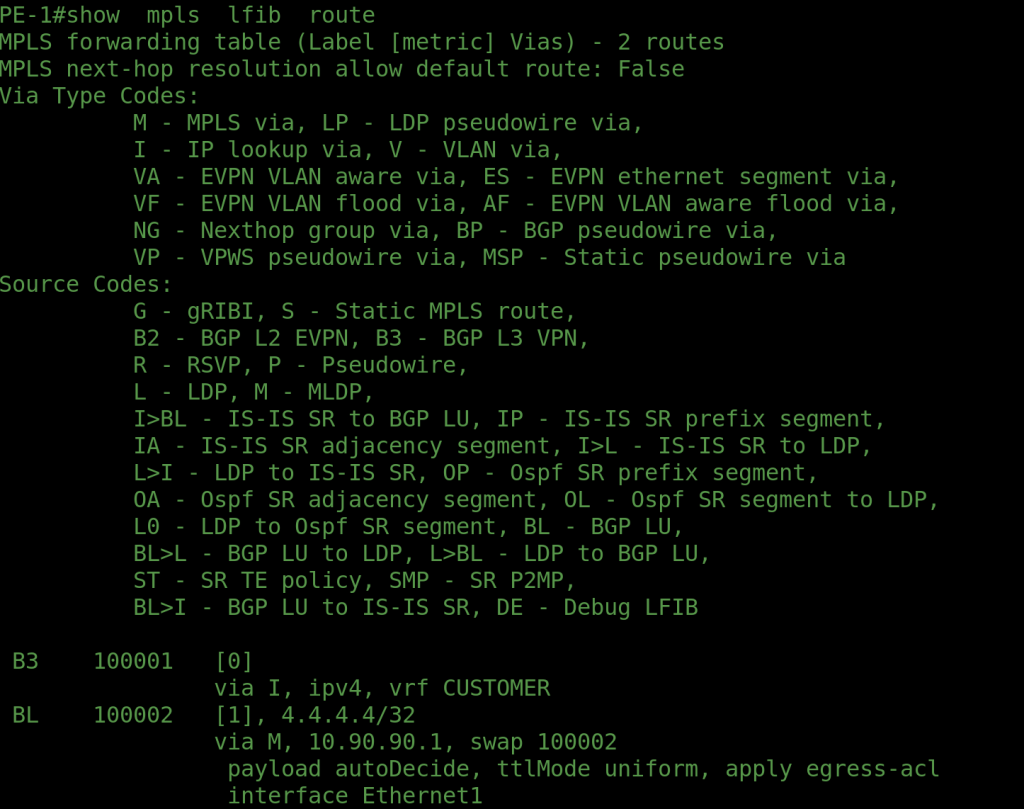
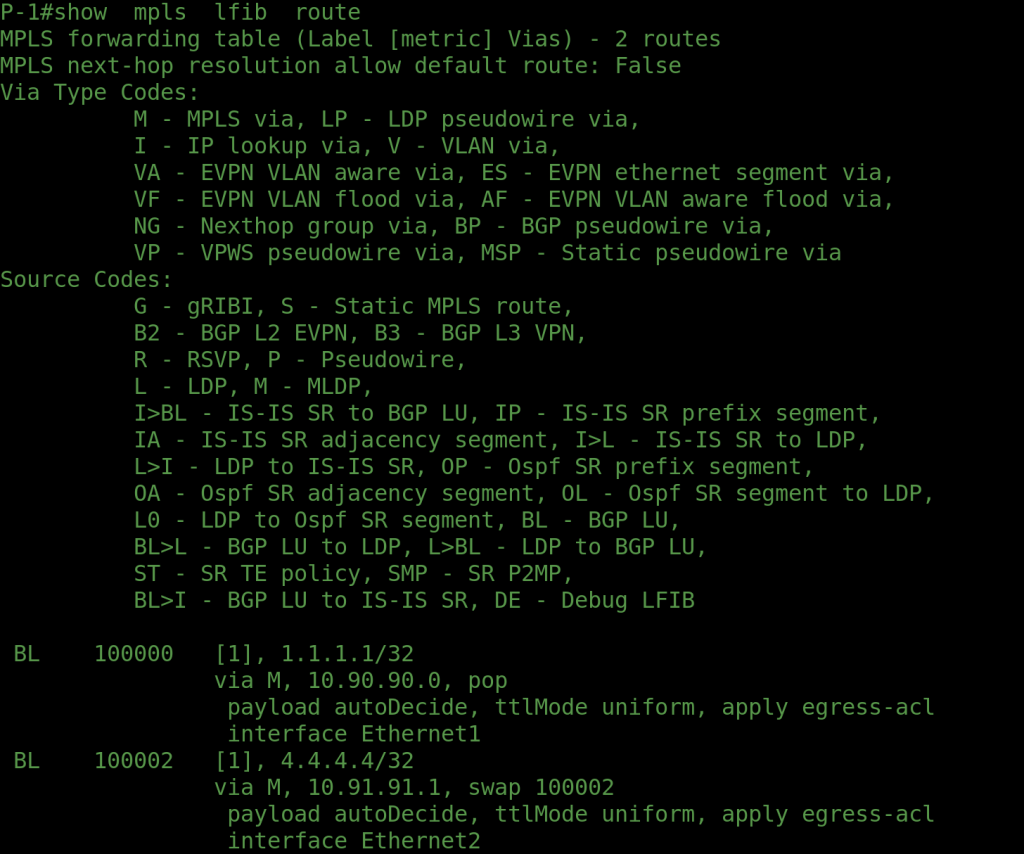
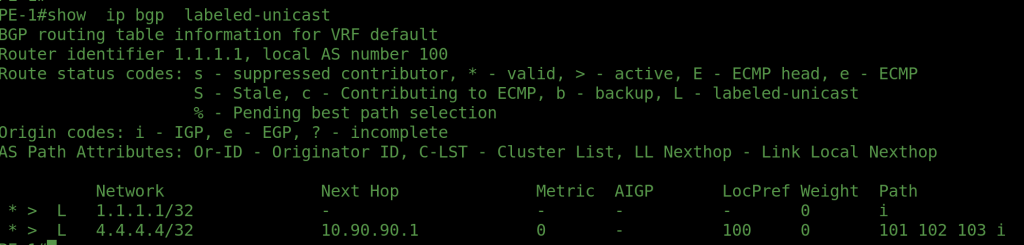
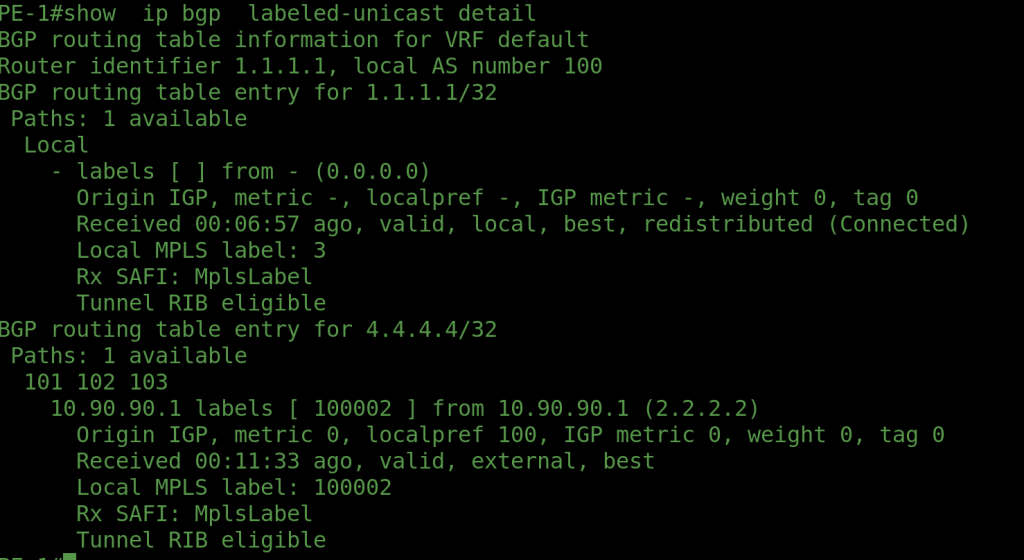
The goal of this design is to advertise only the loopback interfaces of PE1 and PE2 with labels — without announcing any IPv4 unicast routes. Notice in the configuration that we did not establish IPv4 unicast BGP sessions, but instead formed label-unicast peering between all routers. The loopback0 addresses of PE1 and PE2 are advertised using BGP Label Unicast (AFI/SAFI 1/4).
Our ultimate objective is to build an MPLS VPNv4 connection between PE1 and PE2, enabling the exchange of customer VRF routes over the labeled transport path. The corresponding Arista vEOS configuration and verification outputs will be shared in the following section.
Configurations
PE-1
router bgp 100
bgp labeled-unicast rib ip tunnel
distance bgp 20 200 200
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 103
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 4.4.4.4 ebgp-multihop 5
neighbor 4.4.4.4 send-community
neighbor 10.90.90.1 remote-as 101
neighbor 10.90.90.1 send-community
!
address-family ipv4 labeled-unicast
neighbor 10.90.90.1 activate
network 1.1.1.1/32
!
address-family vpn-ipv4
neighbor 4.4.4.4 activate
!
vrf CUSTOMER
rd 1:1
route-target import vpn-ipv4 1:1
route-target export vpn-ipv4 1:1
redistribute connected
P-1
router bgp 101
bgp labeled-unicast rib ip tunnel
no bgp default ipv4-unicast
distance bgp 20 200 200
neighbor 10.90.90.0 remote-as 100
neighbor 10.90.90.0 send-community
neighbor 10.91.91.1 remote-as 102
!
address-family ipv4 labeled-unicast
neighbor 10.90.90.0 activate
neighbor 10.91.91.1 activate
P-2
router bgp 102
bgp labeled-unicast rib ip tunnel
distance bgp 20 200 200
neighbor 10.91.91.0 remote-as 101
neighbor 10.91.91.0 send-community
neighbor 10.92.92.1 remote-as 103
neighbor 10.92.92.1 send-community
!
address-family ipv4 labeled-unicast
neighbor 10.91.91.0 activate
neighbor 10.92.92.1 activate
PE-2
router bgp 103
bgp labeled-unicast rib ip tunnel
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 ebgp-multihop 5
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community
neighbor 10.92.92.0 remote-as 102
neighbor 10.92.92.0 send-community
!
address-family ipv4 labeled-unicast
neighbor 10.92.92.0 activate
network 4.4.4.4/32
!
address-family vpn-ipv4
neighbor 1.1.1.1 activate
!
vrf CUSTOMER
rd 1:1
route-target import vpn-ipv4 1:1
route-target export vpn-ipv4 1:1
redistribute connected
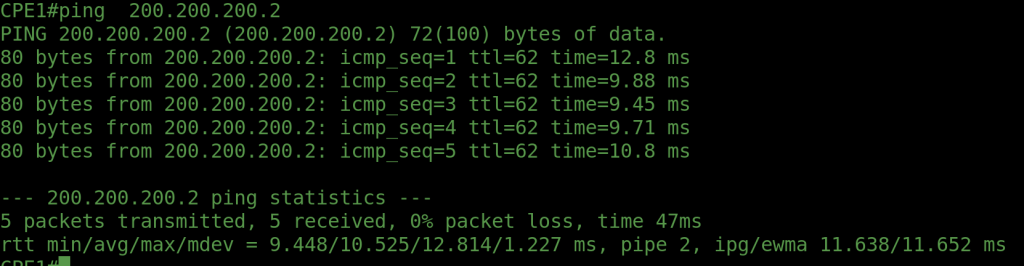
OUTPUTS